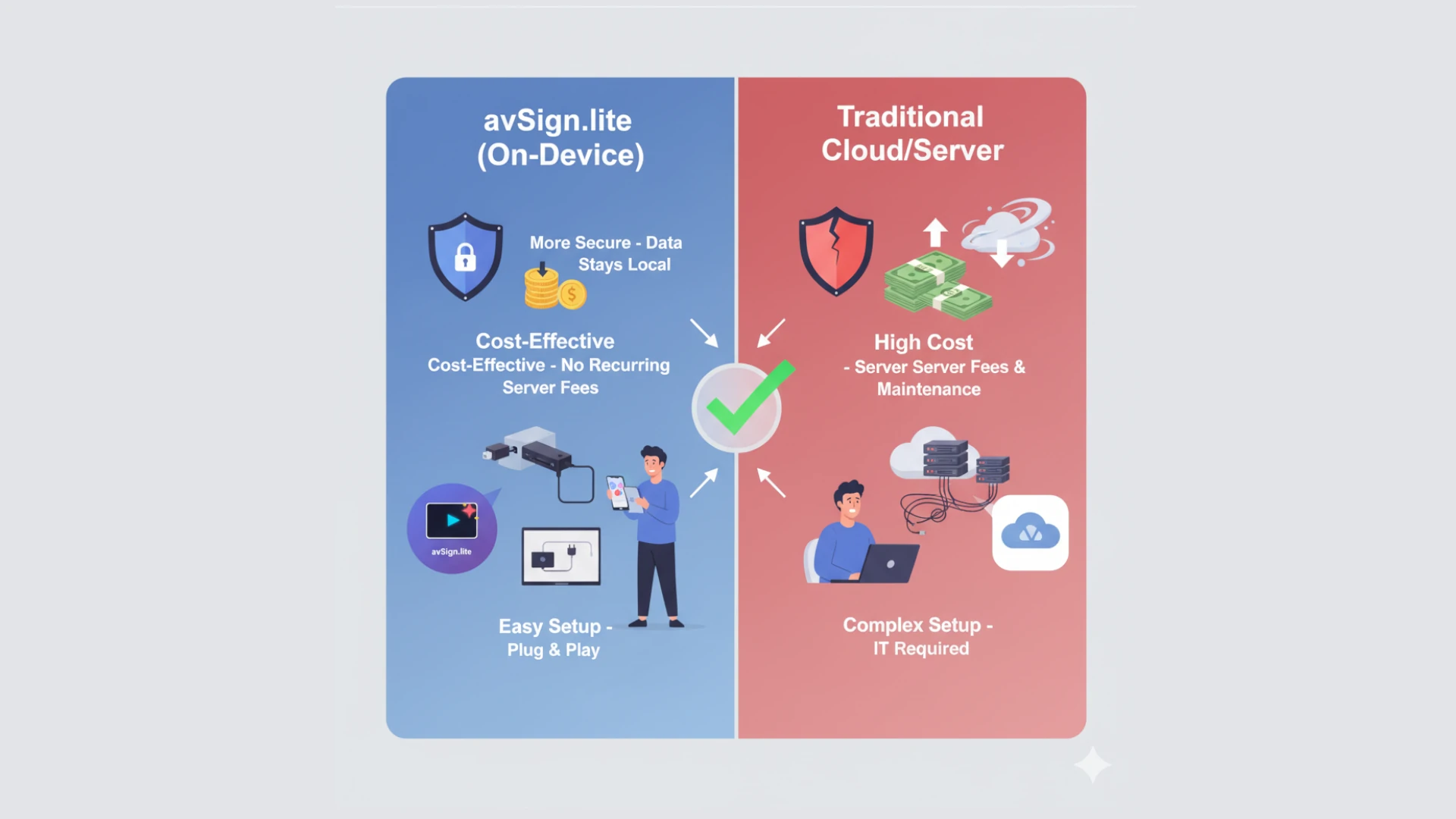
The digital signage industry has evolved significantly over the past decade, with two dominant architectural approaches emerging: traditional cloud-based solutions and modern on-device systems. Understanding the differences between these approaches is crucial for businesses looking to deploy effective digital signage solutions.
The Traditional Cloud-Based Approach
Traditional digital signage platforms rely heavily on constant connectivity to cloud servers. Content is stored remotely, and displays continuously stream data from centralized servers. While this model has been the industry standard for years, it comes with inherent limitations.
How Cloud-Based Systems Work
In a cloud-based architecture:
- Content is uploaded to remote servers
- Displays maintain constant connections to the cloud
- Content is streamed in real-time to each device
- All management and updates happen through cloud services
- Devices become non-functional without internet connectivity
The On-Device Revolution
On-device digital signage represents a paradigm shift in how we think about content delivery. Instead of relying on constant cloud connectivity, modern solutions like avSign.lite store and process content locally on each device.
How On-Device Systems Work
In an on-device architecture:
- Content is downloaded and stored locally
- Displays operate independently of internet connectivity
- Content plays directly from local storage
- Updates sync when connectivity is available
- Devices remain fully functional offline
Performance Comparison
Latency and Response Time
Cloud-Based:
- Subject to network latency
- Content loading depends on bandwidth
- Buffering and stuttering during network congestion
- Degraded performance in low-bandwidth environments
On-Device:
- Zero latency for content playback
- Instant response times
- Smooth transitions and animations
- Consistent performance regardless of network conditions
Content Quality
Cloud-Based:
- Often requires content compression for streaming
- Quality limited by available bandwidth
- Potential for degradation during peak times
- Resolution may be automatically reduced
On-Device:
- Full-quality content playback
- No compression artifacts
- 4K and higher resolutions without compromise
- Pristine visual quality maintained
Reliability and Uptime
Network Dependency
Cloud-Based:
- Complete dependency on internet connectivity
- Single point of failure (network outage = system down)
- Vulnerable to ISP issues
- Service disruptions during cloud provider outages
- Typical uptime: 95-99% (when accounting for network issues)
On-Device:
- Operates independently of network status
- Continues functioning during internet outages
- No dependency on cloud service availability
- Resilient to network infrastructure problems
- Typical uptime: 99.9%+ (limited only by device power)
Real-World Scenarios
Consider a retail store during a major sales event. With cloud-based signage, a temporary internet disruption means blank screens and lost promotional opportunities. With on-device signage, displays continue operating seamlessly, ensuring your message reaches customers when it matters most.
Cost Analysis
Infrastructure Costs
Cloud-Based:
- Monthly/annual subscription fees per screen
- Bandwidth costs for streaming
- Potential overage charges
- Scaling costs increase linearly with screen count
- Hidden costs: increased bandwidth requirements, CDN fees
On-Device:
- One-time license fee (e.g., avSign.lite: $49.99 lifetime)
- No recurring subscription fees
- Minimal bandwidth usage (updates only)
- Fixed cost regardless of screen count
- Predictable, transparent pricing
Total Cost of Ownership (3-Year Comparison)
Cloud-Based Solution (10 screens):
- Setup: $500
- Monthly fees: $50/screen × 10 × 36 months = $18,000
- Bandwidth: ~$500/year × 3 = $1,500
- Total: ~$20,000
On-Device Solution (10 screens):
- Setup: Free
- Lifetime licenses: $49.99 × 10 = $500
- Bandwidth: ~$50/year × 3 = $150
- Total: ~$650
The on-device approach delivers 96% cost savings over three years.
Security Considerations
Data Privacy
Cloud-Based:
- Content stored on third-party servers
- Potential exposure to data breaches
- Compliance challenges (GDPR, data sovereignty)
- Trust required in cloud provider security
- Data transmitted continuously over public internet
On-Device:
- Content stored locally on your devices
- No exposure to cloud-based breaches
- Easier compliance with data regulations
- Complete control over your data
- Minimal data transmission (encrypted updates only)
Attack Surface
Cloud-Based:
- Larger attack surface (cloud infrastructure + network + devices)
- Vulnerable to DDoS attacks on cloud services
- Man-in-the-middle risks during streaming
- Dependency on third-party security practices
On-Device:
- Smaller attack surface (devices only)
- Isolated from cloud infrastructure vulnerabilities
- Reduced exposure to network-based attacks
- Direct control over security implementation
Scalability and Flexibility
Deployment Speed
Cloud-Based:
- Requires reliable internet at each location
- Network infrastructure planning essential
- Bandwidth requirements increase with scale
- Potential bottlenecks at central servers
On-Device:
- Deploy anywhere, regardless of connectivity
- No network infrastructure requirements
- Add unlimited devices without bandwidth concerns
- Each device operates independently
Geographic Distribution
Cloud-Based:
- Performance varies by distance from servers
- International deployments face latency challenges
- May require regional server infrastructure
- Compliance complexity across jurisdictions
On-Device:
- Consistent performance worldwide
- No latency regardless of location
- Simple international deployment
- Easier compliance management
Bandwidth Requirements
Ongoing Usage
Cloud-Based:
- Continuous streaming: 5-50 Mbps per screen
- 10 screens: 50-500 Mbps sustained
- Monthly data: 500GB - 5TB
- Significant impact on network infrastructure
On-Device:
- Initial download: One-time per content update
- 10 screens: 10-100MB per update
- Monthly data: 1-10GB
- Minimal network impact
Network Infrastructure Impact
For businesses with limited bandwidth or multiple locations, the difference is dramatic. On-device solutions eliminate the need for expensive bandwidth upgrades and reduce the strain on existing network infrastructure.
Content Management
Update Mechanisms
Cloud-Based:
- Real-time updates to all screens
- Immediate content changes
- Requires continuous connectivity
- Network congestion affects update speed
On-Device:
- Scheduled or opportunistic updates
- Downloads during off-peak hours
- Updates persist during offline periods
- Efficient bandwidth utilization
Offline Capabilities
Cloud-Based:
- Limited or no offline functionality
- Screens become unusable without connectivity
- No fallback mechanism
- Business continuity risk
On-Device:
- Full offline operation
- Scheduled content continues playing
- No interruption to service
- Business continuity ensured
Use Case Suitability
When Cloud-Based Makes Sense
- Scenarios requiring real-time data integration (stock tickers, live feeds)
- Environments with guaranteed high-speed connectivity
- Situations where immediate, simultaneous updates are critical
- Organizations with existing cloud infrastructure investments
When On-Device Excels
- Retail stores - Guaranteed uptime during business hours
- Restaurants and cafes - Menu boards that work regardless of WiFi
- Remote locations - Limited or unreliable connectivity
- Corporate lobbies - Professional appearance without network dependency
- Trade shows - Deploy anywhere without network concerns
- Cost-sensitive deployments - Budget constraints favor one-time costs
- Privacy-focused organizations - Data control and compliance requirements
The Hybrid Future: Best of Both Worlds
Modern solutions like avSign.lite combine the best of both approaches:
- Primary operation: On-device for reliability and performance
- Optional cloud sync: For convenient multi-location management
- Offline-first architecture: Continues working regardless of connectivity
- Smart updates: Downloads during available connectivity
- Flexible deployment: Works with or without internet
This hybrid approach delivers the reliability and cost-effectiveness of on-device operation with the convenience of optional cloud features.
Environmental Impact
Energy Consumption
Cloud-Based:
- Continuous data transmission requires power
- Cloud server infrastructure energy costs
- Network equipment power consumption
- Higher overall carbon footprint
On-Device:
- Minimal data transmission
- No continuous server load
- Lower network equipment utilization
- Reduced environmental impact
Making the Right Choice
When evaluating digital signage solutions, consider:
- Reliability requirements: Can you afford downtime?
- Budget constraints: Recurring vs. one-time costs
- Network availability: How reliable is your internet?
- Scale: How many screens do you need?
- Privacy concerns: Where should your data reside?
- Performance needs: Do you need guaranteed quality?
For most businesses, the answer is clear: on-device architecture provides superior reliability, lower costs, better performance, and greater control.
Conclusion
While cloud-based digital signage served its purpose in the early days of the industry, the technology has evolved. On-device solutions like avSign.lite represent the future of digital signage—offering the reliability of local operation, the cost-effectiveness of one-time licensing, and the flexibility of optional cloud features.
The choice between cloud and on-device isn’t just about technology—it’s about business priorities. If uptime, cost control, and performance matter to your organization, on-device digital signage is the clear winner.
Ready to experience the difference? Download avSign.lite today and see how on-device digital signage can transform your business. With a 14-day free trial and a one-time $49.99 lifetime license, there’s never been a better time to make the switch.
Questions? Join our Discord community or check out our documentation to learn more about deploying reliable, cost-effective digital signage.